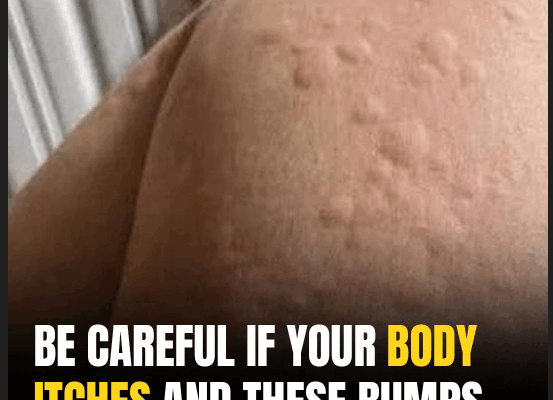
Urticaria, also known as hives, is a common skin condition marked by red, raised, itchy welts that can appear on various parts of the body like the face, arms, legs, and trunk.
These welts vary in size and may cluster together. While they often disappear within hours or days, they can reoccur and affect a person’s quality of life.
Urticaria is caused by the release of histamine and other chemicals from mast cells, leading to fluid leakage from capillaries and the formation of swollen welts.
The main symptoms include hives (raised red or pale lesions), intense itching (pruritus), and an evanescent nature—welts usually vanish within 24 hours without leaving a mark. In some cases, urticaria may be accompanied by angioedema, a deeper swelling that can affect areas like the hands, lips, eyelids, or throat, the latter being a medical emergency.
Urticaria is classified by duration: acute urticaria lasts less than six weeks and is often triggered by allergens, infections, or medications, while chronic urticaria lasts longer and may have no identifiable cause. Physical or inducible urticaria results from stimuli like pressure, cold, heat, sunlight, or stress. Diagnosis is based on a patient’s history and physical exam, with treatment aimed at managing symptoms and avoiding triggers. Antihistamines are the first line of treatment, while corticosteroids may be used in more severe or chronic cases. Avoiding known triggers is key to managing the condition.