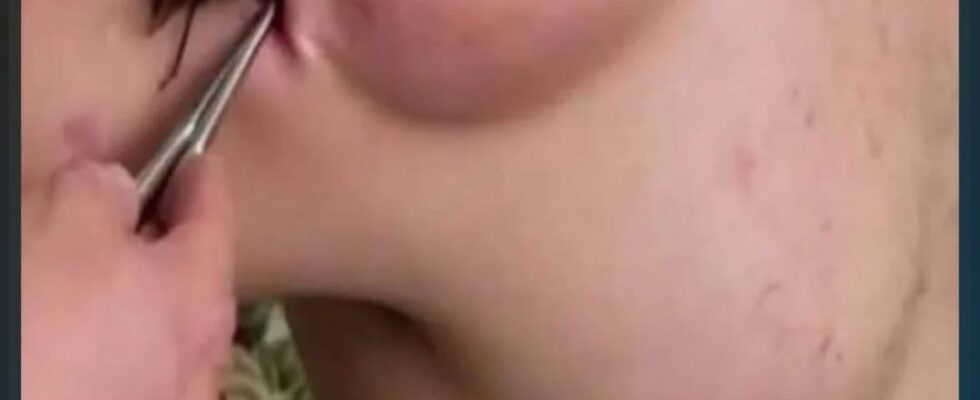
When a bee stings a person, the bee injects venom through its stinger into the skin.
This venom contains proteins that affect skin cells and the immune system, causing pain and swelling at the site of the sting.
Here are the typical steps and effects: Immediate Pain: The sting causes a sharp, burning pain right away because of the venom and the physical puncture.
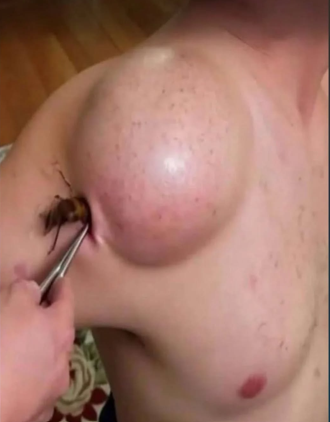
Redness and Swelling: The area around the sting usually becomes red, swollen, and warm as the body reacts to the venom.
Itching and Irritation: After some time, itching or irritation often develops around the sting site.
Inflammatory Response: The immune system responds by sending white blood cells to fight the foreign venom, which causes inflammation.