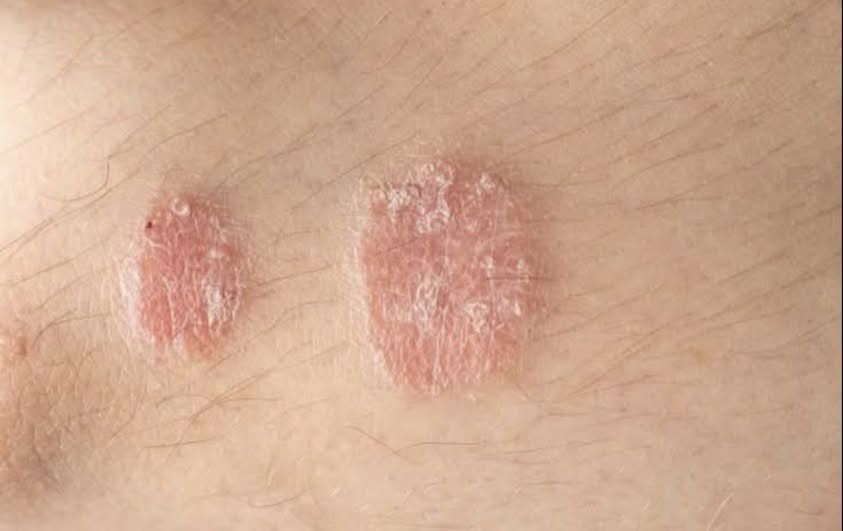
Plaque Psoriasis, marked by red patches with silvery scales; Guttate Psoriasis, characterized by small, drop-shaped spots; Pustular Psoriasis, featuring red skin with pus-filled blisters; Inverse Psoriasis, which affects moist skin folds; and Erythrodermic Psoriasis, a severe, emergency condition with widespread redness and peeling, It’s not communicative. Genetic factors and immune system dysregulation, in which T-cells target healthy skin cells, are among the causes. Infections, alcohol, and other drugs are common triggers. A physical examination and occasionally a biopsy are used to make the diagnosis. Treatments can control symptoms and enhance quality of life even though the condition is incurable
If you notice this….